Kunming, China, February 10, 2017
Our studies utilize world-class imaging technologies that are available at KBI, as well as, through our extensive external network collaboration with experienced clinical imaging experts and medical institutions that enable us to have greater access to a wide variety of extraordinary instrumentation and expert technical advice.
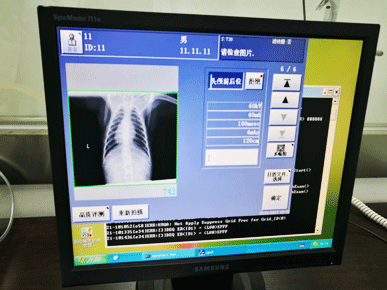
X-Ray Imaging
At KBI, non-invasive radiography is utilized for diagnostic imaging, as well as, for longitudinal in vivo follow-up imaging of disease progression or pharmacological efficacy response in our study animals and NHP disease models.

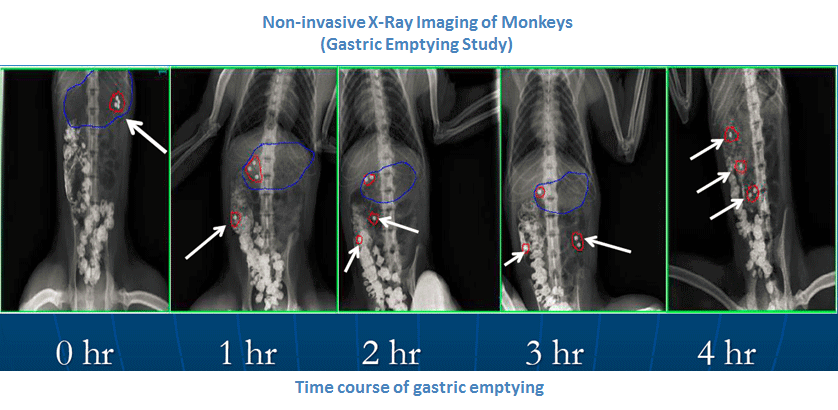
Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) is a non-invasive analytical method that provides quantitative information about whole body (total mass), fat and fat-free/bone mass composition for metabolic research studies as well as bone mineral content (BMC) and bone mineral density (BMD) which are important determinants of bone strength.
At KBI, the DEXA is utilized as a diagnostic and evaluation end point for metabolic research and osteoporosis studies. In addition, longitudinal in vivo scans are a powerful tool to examine treatment-induced changes that develop over time.
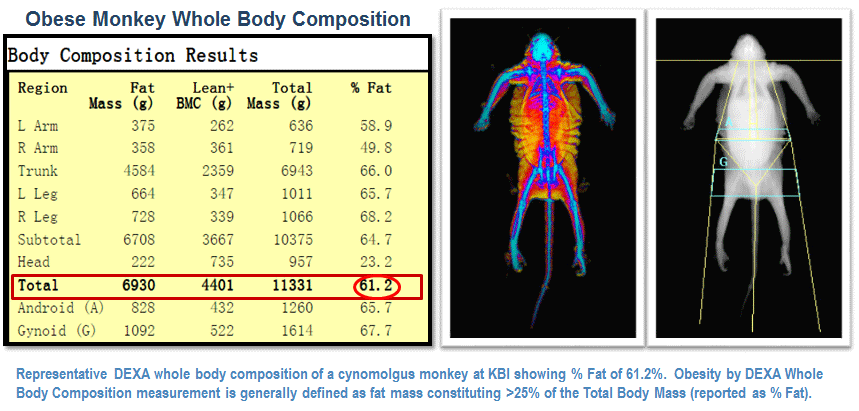
Using the HOLOGIC Discovery QDR® Series (Fan-beam) and Hologic Body CompositionSoftware (Version 13.3.0.1 Auto Whole Body-Hologic), the composition of the following body compartments are analyzed and estimated: Total Body Fat Mass, Lean Mass, Percentage Body Fat, Bone Mineral Content (BMC) and Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
(Results from whole body composition and precision validation data are available upon request)
Ultrasound Imaging
KBI is equipped with a compact console ultrasound system that has a wide range of diagnostic, therapeutic, interventional, and screening applications. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous tissue biopsies can be performed routinely at KBI. Furthermore, KBI has formed an effective network with non-invasive cardiology/echocardiography consultants and local medical institutions/hospitals for access to technical expertise and advanced cardiac ultrasound-2D echocardiographic equipment with analytical workstations in support of cardiac studies requiring screening and serial follow-up of our NHP cardiovascular disease models.
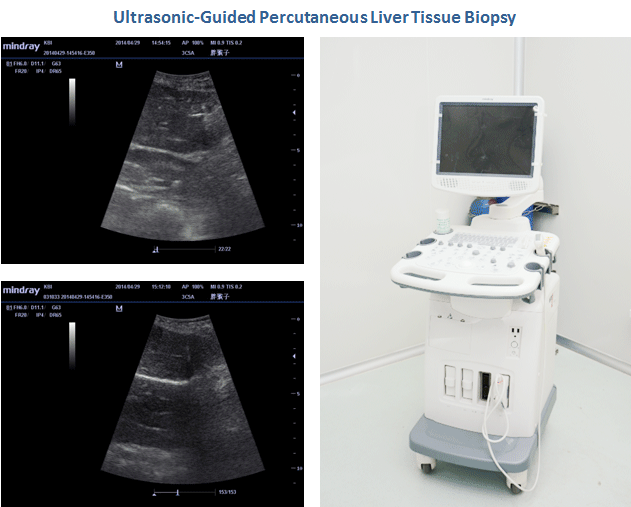
Endoscopy
At KBI, gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy is performed to enable direct visualization and screening of disease-specific morphologic or functional tissue alterations in NHP cohorts with characteristic clinical signs of chronic or recurrent inflammatory bowel disorders. Endoscopy is also used for longitudinal visual assessment of disease activity in our NHP Inflammatory Bowel Disease models for efficacy evaluation studies.

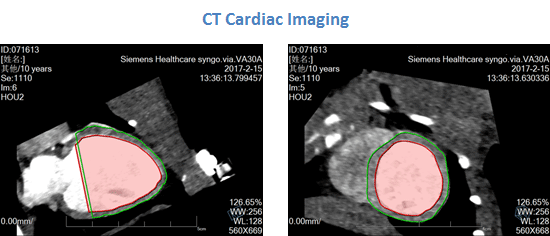
Computed Tomography (CT)
KBI utilizes computed tomography of the heart (or cardiac CT) to perform assessments of the cardiac or coronary anatomy, evaluate volumetry and cardiac function (including ejection fraction); and, to detect and monitor the progression of coronary artery disease (CAD) or heart failure in our NHP cardiovascular disease (CVD) models.
Furthermore, Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) can be applied to characterize and monitor our NHP atherosclerotic CVD models for the following applications: detection of thrombus, plaque, and intimal calcifications, as well as, measurement of vessel luminal diameter; acquisition of quantitative info on the caliber and course of normal and abnormal arterial segments; and, characterization of atherosclerotic plaque severity, composition, and potential ulcerations.
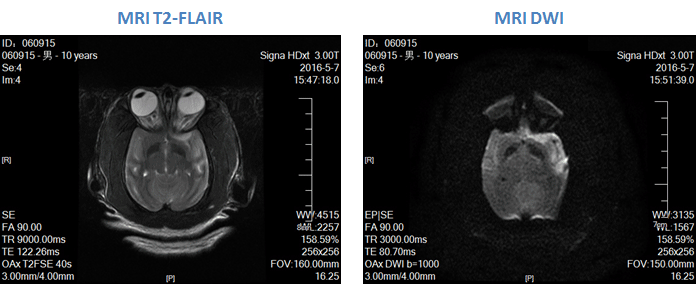
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
KBI has access to state-of-the art MRI facility and utilizes this platform as a stand-alone or complementary preclinical imaging technique for a variety of preclinical research needs that require sensitive in vivo measurements of structure or function of tissues. KBI utilizes the MRI for high spatial resolution imaging optimized for neuroscience research as well as for models of obesity (e.g., fat segmentation and quantification), cardiovascular disorders and atherosclerosis, NAFLD and NASH and, bone and joint inflammatory models. Furthermore, MRI is also used as an effective non-invasive imaging tool with applications for the evaluation of pharmacological interventions in many of our translational NHP disease models.
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Molecular imaging enables the study of molecular and cellular processes in vivo. Within this field, the Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) have been distinguished as established techniques that are based on the detection of injected radiolabeled probes. These nuclear imaging modalities have in vivo applications for targeting ongoing biochemical processes to explain molecular interactions important in the onset and progression of disease, to investigate the biologic relevance of drug candidates, and to monitor the therapeutic effectiveness of pharmaceuticals within a single-model system. PET extends use of the 18F-FDG and other positron-labeled biologic tracers into the preclinical realm as a biomarker for pharmaceutical development and for metabolic studies in the biologic sciences.
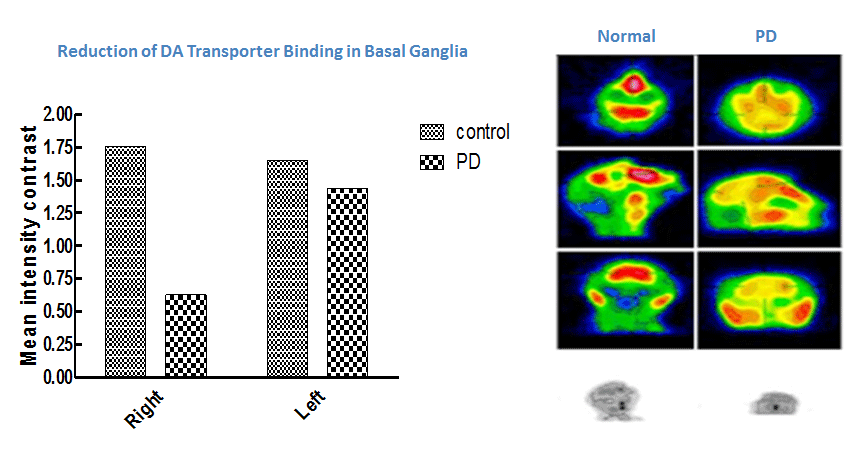
At KBI, the radioisotope tracer, 99mTc-TRODAT-1, which selectively binds to the dopamine (DA) transporter, is used with SPECT imaging to visualize nigrostriatal dopaminergic nerve terminals and demonstrate the reduction of DA transporter binding in the basal ganglia of NHP models of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease.

Contact us if you need more information.